In the modern healthcare center, power supply is not merely an operating necessity, but a savior. Do hospitals have emergency generators? Yes. As public institutions of life and death significance, hospitals ought to be equipped with stable and dependable backup power supplies to deal with the unexpected loss of electricity and ensure patient safety and continuity of medical attention.
Today, we will walk you through the functioning of hospital emergency power systems and highlight the critical significance of such essential items as the spring starter in ensuring reliable emergency power.
Part 1. Why Hospitals Require Emergency Power Systems?
Hospitals are very power-hungry buildings where even a single second’s power outage can result in catastrophic consequences. Here’s why a reliable emergency power system is not a luxury, but a necessity:
Life Support Systems Cannot Be Disrupted
Life-saving equipment that includes ventilators, cardiac monitors, infusion pumps, and defibrillators is heavily used in critical care units such as ICUs and ERs.
These are always running 24/7 and, in some cases, are the only reason why patients who are severely ill or injured are being kept alive. Disruptions in power can lead to immediate life-threatening scenarios.
Operating Rooms Need Uninterrupted Power
A sudden loss of power during surgical interventions would be disastrous. Illumination during surgery, electrosurgical equipment, anesthesia units, and patient monitors must be uninterrupted. A disruption even for a moment could compromise patient safety and outcome.
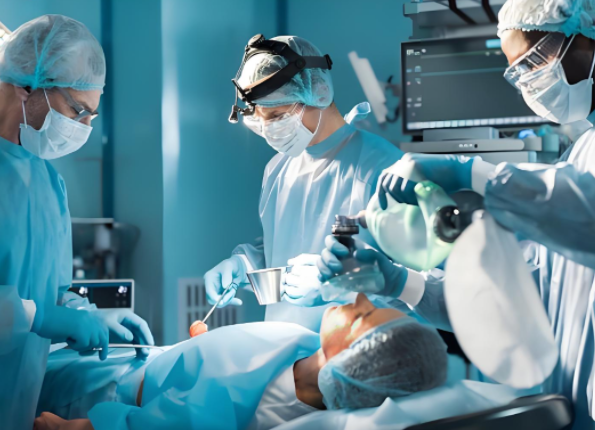
Medication Storage and Electronic Medical Records Depend on Power
The majority of critical medicines, vaccines, and blood stocks must be kept at precise temperature ranges by the implementation of powered refrigeration. In addition, modern hospitals utilize electronic health records (EHRs) to access patient information immediately. Electricity loss could compromise access to drugs and critical information.
Critical Facility Operations Rely on Electricity
Apart from clinical equipment and devices, most facility systems require electricity to function optimally, such as lighting, elevators, HVAC, water pumps, and communications. Disruption of these might result in hindering response efforts during emergencies and overall hospital safety.
Due to these considerations, hospitals must, both legally and ethically in most areas, have very reliable emergency generator systems. These systems have to be able to come on instantly and power the hospital for prolonged time periods, allowing the hospital to safely function when there is an outage.
Part 2. Do All Hospitals Have Emergency Generators?
In all countries, including the United States of America, regulations such as NFPA 110 mandate that medium and large hospitals have effective backup power supplies, preferably emergency generators running on diesel. The backup power systems are designed to automatically come on in seconds during blackout and feed electricity into hospital sections that are most crucial.
But not all medical facilities are equal. Some rural health outposts or smaller private clinics may not have whole-facility generator systems. They may only have limited UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) units or portable generators, which can only drive vital equipment for a short period of time.
To offer redundancy, huge hospitals employ duplicated power supplies, such as a main generator, backup generator, and UPS systems. The multi-layered system ensures guaranteed functioning of critical hospital operations, such as ICUs, operating rooms, and emergency lights in any and all circumstances.
Part 3. What Types of Emergency Generators Do Hospitals Employ?
Hospitals typically employ several types of emergency power systems, each infrastructural size-specific, size-specific, and energy-specific to their own:
1. Diesel Generators (Most Popular)
Diesel generators make up the bulk of hospital backup power. They deliver high output capacity, anything between a few hundred kilowatts and some megawatts, and are most ideal for large-sized, critical institutions. Diesel generators are renowned for:
- Easy fuel availability and easy on-site storage;
- High dependability and long lifespan when utilized over extended periods of time;
- Quick start-up, reducing time for power disruption.
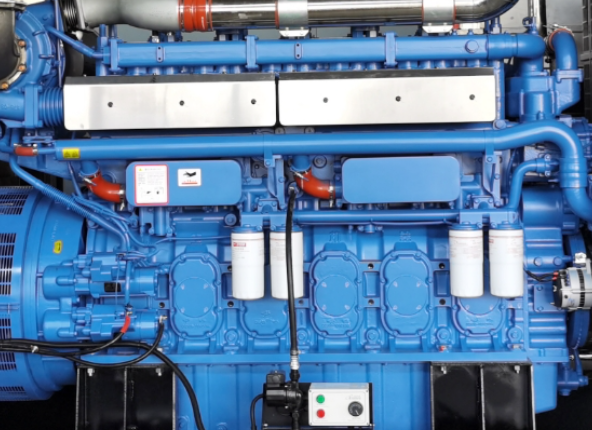
2. Natural Gas Generators
They are valued for being greener and less polluting. They’re typically piped from city gas mains, which offers no requirement for fuel storage. However:
They rely heavily on sustained supply of gas, which can be compromised due to natural disasters.
3. Battery Backup + UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply)
Used to fill the gap in the brief interval until the main generators become operational. UPS systems:
- Cover immediate power to critical equipment like servers, monitoring systems, and operating rooms;
- Offer uninterrupted power continuity and allow generators time to warm up correctly.

4. Hybrid Systems
New hospitals increasingly employ hybrid systems that integrate diesel, natural gas, solar, and battery storage to:
- Maximize energy efficiency;
- Increase resilience and sustainability;
- Reduce long-term operating costs.
The capacity and dimensions of emergency generators depend on the dimensions of the hospital, patient population, and nature of its critical facilities—typically in the range of a few hundred kilowatts for small clinics and a few megawatts for big city hospitals.
Part 4. How Do Hospital Backup Power Systems Work?
Hospital emergency power systems are designed to immediately and dependably react when there is a failure in the main power supply. At the center of this system is the Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS), which is always monitoring the main power supply.
When the main power fails, the ATS starts the backup power process, typically within 10 seconds or less, to ensure as minimal interruption as possible to critical operations.
Simplified workflow breakdown:
Power Failure Detection
The ATS continuously monitors the incoming utility power. The moment it detects a loss or dip below reasonable voltage levels, it starts the backup system.
ATS Powers Up Emergency Generator
The ATS outputs a start signal for the emergency generator, which may be powered by diesel, natural gas, or a hybrid setup.
When the generator is at operational speed and voltage stability, the ATS switches the hospital’s electrical load to the generator. The electricity is restored to critical loads like life-support systems, lighting, operating rooms, and IT hardware.
Utility Power Restored
The ATS switches back to the utility supply when it detects that main power is stable again.
Generator Shutdown
After a short cooling period, the emergency generator switches off automatically, returning the system to standby.
At all times during all this, stable start-up of the generator is vitally critical. Even temporary failure to start can lead to life-critical interruptions. This is why some hospitals include mechanical devices like spring starters as a fail-safe measure so the generator can start regardless of batteries or electronics alone.
Part 5. Why is Emergency Generator Maintenance So Important?
Hospital emergency power systems are not “install and forget” machines. To operate successfully during an actual loss of power, routine maintenance and testing are essential. Proper maintenance is essential to ensure that the system does not fail miserably, even harming patients’ lives and operations in the hospital.
Main maintenance procedures are:
Monthly Start-Up Tests:
The starter is engaged and run for a limited duration monthly to test whether it is able to start smoothly and operate without any fault. This helps in early identification of faults like battery depletion or fuel clogging in the system.
Quarterly Load Tests:
In controlled environments, the generator operates at or below its maximum rated load. This ensures that it can provide the hospital’s actual power loads during power outages and all systems operate well under stress.
Routine Inspections:
They monitor key items such as engine oil level, fuel condition, battery voltage, coolant, and control system parameters regularly. Monitoring these in a regular pattern detects wear or imminent failures before they occur.
Simulated Power Outages:
Routine drills for simulated power outages allow hospital staff to test not only the generator’s response but also the automatic transfer switch and emergency protocols. Routine drills keep them ready and expose any system weaknesses.
Part 6. How Spring Starter Can Help Emergency Starting?
Spring starters offer a reliable and battery-less starting system for diesel generators, especially in severe environments, remote locations, and mobile medical vehicles. Compared to traditional electric starters based on battery power, which are exposed to temperature extremes, charging deficits, or prolonged storage—spring starters utilize hand-wound mechanical power to efficiently and safely start engines.
Our Cqstart Spring Starter has the power to start large diesel engines with up to 50-liter displacement, making it ideal for use in emergency rescue vehicles, temporary disaster clinics, military field hospitals, and other demanding applications.
Key Features of Cqstart Spring Starter
Battery-Free Operation: Manual winding system abolishes reliance on batteries to ensure safe starts when electrical systems malfunction.
High Compatibility: Suitable for 50L diesel engines, providing a wide range of large generator applications.
Hard and Low Maintenance: Mechanical ruggedness ensures low maintenance requirements and maintains performance after extended storage periods.
Ideal for Harsh Environments: Suitable for mobile hospitals, emergency response, and military field clinics where power integrity is critical.
Redundant Safety: Provides fail-safe redundancy to traditional electric starters, providing an added layer of safety for emergency power systems.
With the use of Cqstart spring starters in emergency power setups, hospital personnel can deliver consistent, reliable generator starts under the most challenging circumstances—saving lives where they’re needed most.

Final Words
Hospitals simply can’t afford to be taken down by power failures. A perfect emergency power system should include the following elements:
- Main power supply + UPS + backup generator;
- Automatic transfer switch + startup on the fly;
- Rugged generator equipment + backup starting solutions (e.g., spring starters);
- Routine maintenance and testing procedures.
In all organizations committed to safeguarding lives, emergency power is not an option, it’s mandatory.
If you are in the emergency power equipment or starter-related industry, consider focusing on high-quality application markets such as hospitals, mobile medical vehicles, and disaster response. The spring starter may be the standby starting solution they are searching for.

